Nearly everyone has heard of cryptocurrency mining, but what exactly is it? Mines are nothing more than the creation of new blocks in the blockchain of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. However, a consensus is needed on the network to create blocks on the chain. The most common method to achieve it is the Proof of Work algorithm.
The workings of cryptocurrencies are based on cryptography. The science involves secure communication between one entity and another through constructing and analyzing protocols that allow privacy without interference from third parties. With cryptocurrencies, the key elements of a transaction are its confirmation. This is where the consensus algorithm comes into play.
Table of Contents
The Proof of Work – What is it?
The Proof of Work algorithm is the most common method of confirming a transaction. The PoW is a system primarily designed to protect and prevent attacks. The market for cryptocurrencies today is worth hundreds of billions of dollars, so each transaction made on the blockchain must be checked and verified to be considered safe.
A Proof of Work is a cryptographic proof of work with zero knowledge. So what is proof of work with zero knowledge? It is when one party can prove to another that it has a certain piece of information without revealing its contents. This is useful especially in authentication processes, particularly when anonymity is required. It sounds like the definition of a cryptocurrency transaction, right?
The mining race
As its name suggests, the Proof of Work requires work, which will later be rewarded. The confirmation of transactions is handled by miners. And how is this done? By using high computing power, the computers solve complex cryptographic calculations.
Simply put, the miners compete with each other as to which of them is the first to solve the problem (known as a hash). Every time a miner confirms a transaction through a successful calculation, he receives a reward in the form of cryptocurrency from the network where he works.
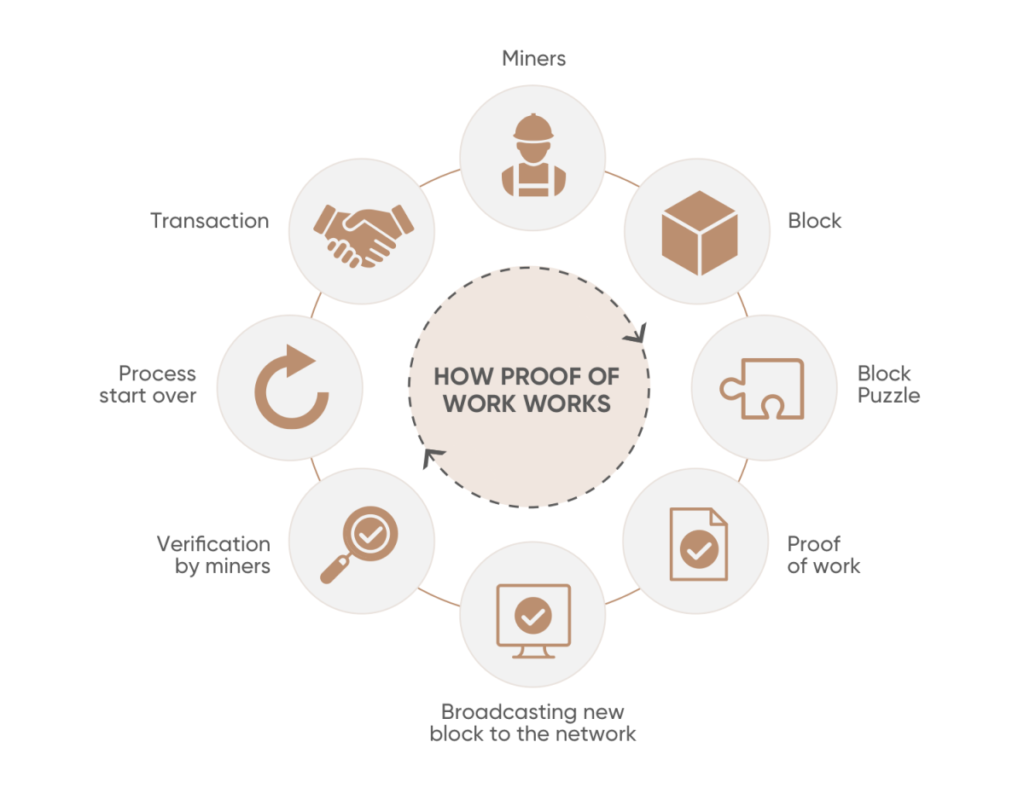
How proof-of-work works
A blockchain is a shared ledger containing the history of all past transactions. As its name suggests, it is made up of blocks that store the history of recent transactions.
A proof-of-work is required to add new blocks to the blockchain, and the blocks are created by a miner who performs a proof-of-work. Every time a miner successfully performs a proof-of-work (after winning a competition between many other miners), another block is added to the network. This occurs approximately every 10 minutes.
A successful proof-of-work is very difficult and requires expensive dedicated computers for miners to generate blocks and earn bitcoins. And the more operations they can perform, the more bitcoins they can win.
What operations do the miners perform?
In Bitcoin, the miners produce so-called hashes of input values into a random string of alphabetic and numeric values.
The likelihood that a given miner can produce the latest bitcoin hash is very low. But miners worldwide perform such operations tens of thousands of times per second, making an average hash in about 10 minutes.
The first miner to successfully perform the operation gets a bitcoin. Bitcoin’s protocol then creates a new value that the miner has to hash, with the miner restarting the race for a successful proof-of-work.
History of PoW
The theory of Proof of Work was presented by Cynthia Dwork and Moni Naor in 1993, while the term itself was coined in 1999 by Markus Jakobsson and Ari Juels.
The use of the Proof of Work concept in finance was proposed by Hal Finney in 2004. Legendary cryptographer introduced his idea as “multiple uses of proof of work”. 5 years later, his idea was implemented in the Bitcoin blockchain, with Finney being the recipient of the first transaction on the BTC network.
The same consensus algorithm has been used as the basis for such well-known cryptocurrencies as Litecoin, Monero, Bitcoin Cash and Ethereum (although the team developing this cryptocurrency is still working on the transition to Proof of Stake).
Pros of Proof of Work
The proof of Work algorithm has found its way into cryptocurrencies. It is still used today by many of them for several key features:
Security
PoW guarantees secure and seamless transactions, a fact confirmed by more than a decade of use in cryptocurrencies.
Scalability
Because of many miners, the Proof of Work algorithm is highly scalable and applicable to many applications.
Cons of Proof of Work
Second-generation cryptocurrency originators, though, are seeking other solutions, as Proof of Work has limitations not found in other trade confirmation algorithms:
High Costs
PoW opponents’ first argument is that this algorithm requires a lot of energy. Many scientists believe that Proof of Work is a completely unnecessary waste of computing power. Significant energy expenditure also hinders cryptocurrencies from mass adoption.
51% Attack
To add malware to a blockchain based on Proof of Work, the hacker needs a computer with more than 51% of the network’s total computing power. While this is basically impossible for large cryptocurrencies, the smaller PoW-based crypto is vulnerable to this type of attack.
Alternatives to PoW
The flaws and limitations of the Proof of Work algorithm mean that cryptographers are working on different methods of verifying transactions. The most common alternative to PoW is Proof of Stake (PoS).
In the PoS algorithm, miners do not compete, as the creator of a new block is chosen by the algorithm based on the stake inserted. ‘Proof of Stake’ is also much less vulnerable to 51% attacks, as a hacker must have 51% of all the cryptocurrency created so far to carry out such an attack.
That’s not all the existing algorithms for achieving network consensus, however. In time, they have also been developed:
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
- Leased Proof of Stake (LPoS)
- Proof of Activity (PoA)
- Proof of Capacity (PoC)
- Proof of Importance (PoI)
- Proof of Burn (PoB)
- Proof of Weight (PoWeight)
And many, many others.
Despite inventing more consensus algorithm concepts, cryptocurrencies based on the Proof of Work algorithm are still being created.
This is primarily because the practical application of this solution is known and tested. While there are alternatives, PoW remains the most popular algorithm in cryptocurrencies. It looks like this will not change for a long time.