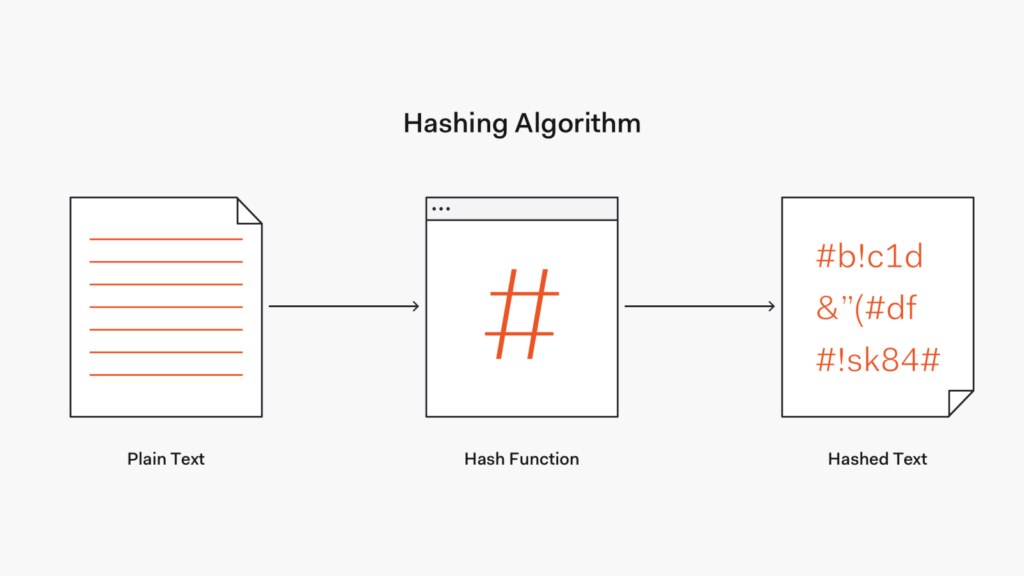
Hash is a term used primarily in mathematics and computer science. It is not used to refer to marijuana, as is often the case. The hash is derived from the English verb to hash, meaning chop something up or scatter something. In principle, a hash value is indicated by hash.
One hash value combines a variety of information that is assigned via a hash function, whereby the hash function can transmit a string of characters of any length. We will explain what this is all about in more detail in this blog post.
Table of Contents
Hashes and the hash function
Suppose you have a large bowl with many different three-dimensional geometric figures in many colors. You would like to sort the figures by color. Therefore you have many smaller shells, each representing one color. You have a bowl for red figures, a bowl for blue figures, one for yellow figures, and so forth.
Now begin to distribute the geometric figures by color into each smaller bowls. One red cuboid goes into the bowl for red figures, a yellow cone goes into the bowl for yellow figures, and one blue sphere goes into the bowl for blue figures. After emptying the large bowl and distributing the figures to the individual bowls, you have accomplished exactly what a hash function can do, among other things.
A hash function, which would be you in the example above, maps a large amount of incoming information, that is, the large shell with the many different three-dimensional geometric figures, into hash values, where hash values represent the smaller shells.
The hash function recognizes the features, in the example, these are the colors, and assigns the information, fully automatically, to the respective hash values. Ideally, a working hash function is characterized by the following features:
- Equal distribution of the hash values to input values
- The size of the hash value does not exceed the size of the assigned information
- Similar information is assigned to different hash values
- Efficiency
- Every hash value has information assigned to it
- Order preservation by, e.g. algorithms
Hash functions are used, for instance, in data storage, information integrity checks, checksums, and cryptology.
The hash in the data storage
In the area of data storage, information is stored in databases. Databases are commonly used to store large amounts of data. For example, this relates to the customer information of a crypto exchange. Information such as name, street address, birth date, email address and telephone number can be assigned to a hash value in a database using a hash function.
When John Old, living in New Jersey, born on 11.11.2011 with the mail address johnold@gazettely.com and the phone number 757 1234567 registers, all the information is assigned to the hash value 1. 1 then means the amount of information that John has disclosed. John gets his unique key for transmitting the information, so his data can be assigned correctly. Various key methods can be used to encrypt and decrypt the data.
The Hash in Checksums
Checksums have the function of verifying the authenticity of the information. That plays a large role in the range of data protection and data communication. Checksums can detect errors in data transmission and correct them if necessary.
A checksum is calculated during data transmission, starting from the sender, and transferred with the data. The recipient can now calculate the checksum of the transmitted data itself and compare its own checksum with the transmitted checksum. This enhances the possibility of assigning information about a function to the correct hash values.
When John wants to change his address in his account at the crypto exchange, it is possible to create a checksum from the address. The checksum matching increases the probability that the new address is really assigned to John’s account.
The Hash in Cryptology
A cryptologic hash function exists when a hash function works only in one direction, and it avoids possible collisions, including those caused by hacks. A collision occurs when two pieces of information are assigned to the same hash value. Then an error is present. A collision could lead to John being able to access Marie’s account, which shouldn’t happen if possible.
The purpose of cryptographic hash functions is to provide additional security through their one-sided direction of use. Algorithms are mostly used for this purpose in cryptography. They form the basis for asymmetric crypto systems, among other things.
These systems are asymmetric because no common, private key is used; rather, it is the database operator who has a secret key and provides a public key. The method is also known as public key infrastructure (PKI). Cryptological hash functions are also used in crypto mining.
Mining algorithms
Arguably, the most well-known mining algorithm is the SHA256 algorithm, used for Bitcoin mining. The speed of application of the algorithm is expressed in hash power. High hash power exists, for instance, if 300 terahash (300 TH/s) can be calculated per second.
Hashpower is calculated by the speed with which source information, that is, John’s and Marie’s address data as a comparison, is calculated against each other. Here, this principle applies: the more computing power a computer provides, the quicker source information can be assigned hash values.
In bitcoin mining, the source information of a transaction, such as sender and amount, is allocated to the receiver, in this case, the hash value, through the blockchain (What is blockchain?). As more computers receive the same checksum, the transaction is more likely to have occurred.
Therefore, what happens is that the more hash power a computer provides, then the more transactions it can process per second. Similarly, our computer is more likely to receive a reward for finding a block that consists of a defined number of transactions, given the more transactions it can compute per second.
Therefore, depending on the amount of hash power a computer has, it can process more transactions per second.
Also Read:
- All You Need to Know about Bitcoin and Other Cryptocurrencies: Mining, Buying, Understanding
- Binance Review (2022): Is It the Best Crypto Exchanges Out There?
Conclusion: What is hashing?
Hashing play a major role in the correct mapping of information to destinations. They are used in databases, testing procedures and particularly secure transmission processes from the cryptographic field. Inside the cryptographic field of mining, Hashes form the basis for digital, encrypted value creation and value transfer processes. Bitcoin is just one example of many in which they are used.